Cover Photo © Hernan Povedano
Description
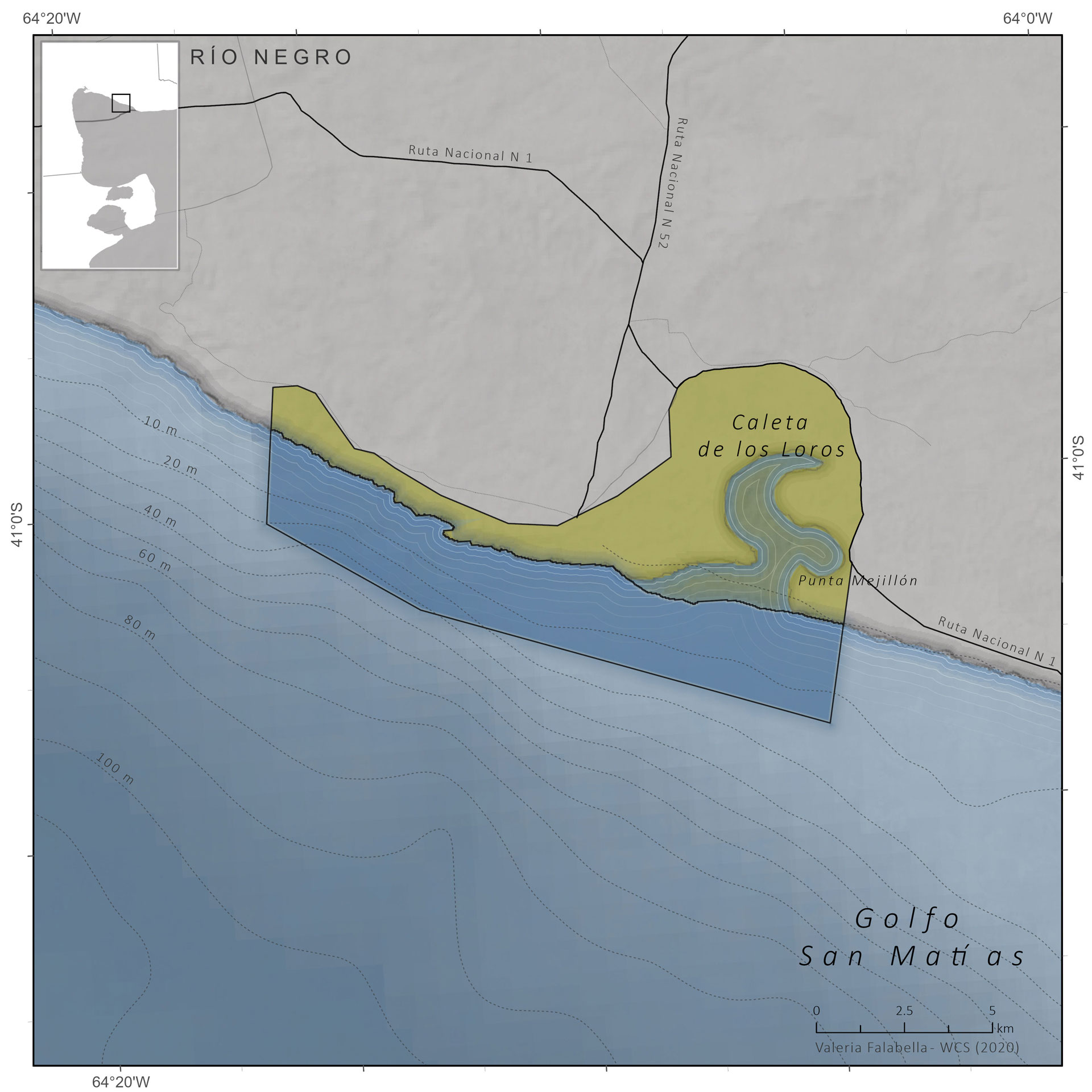
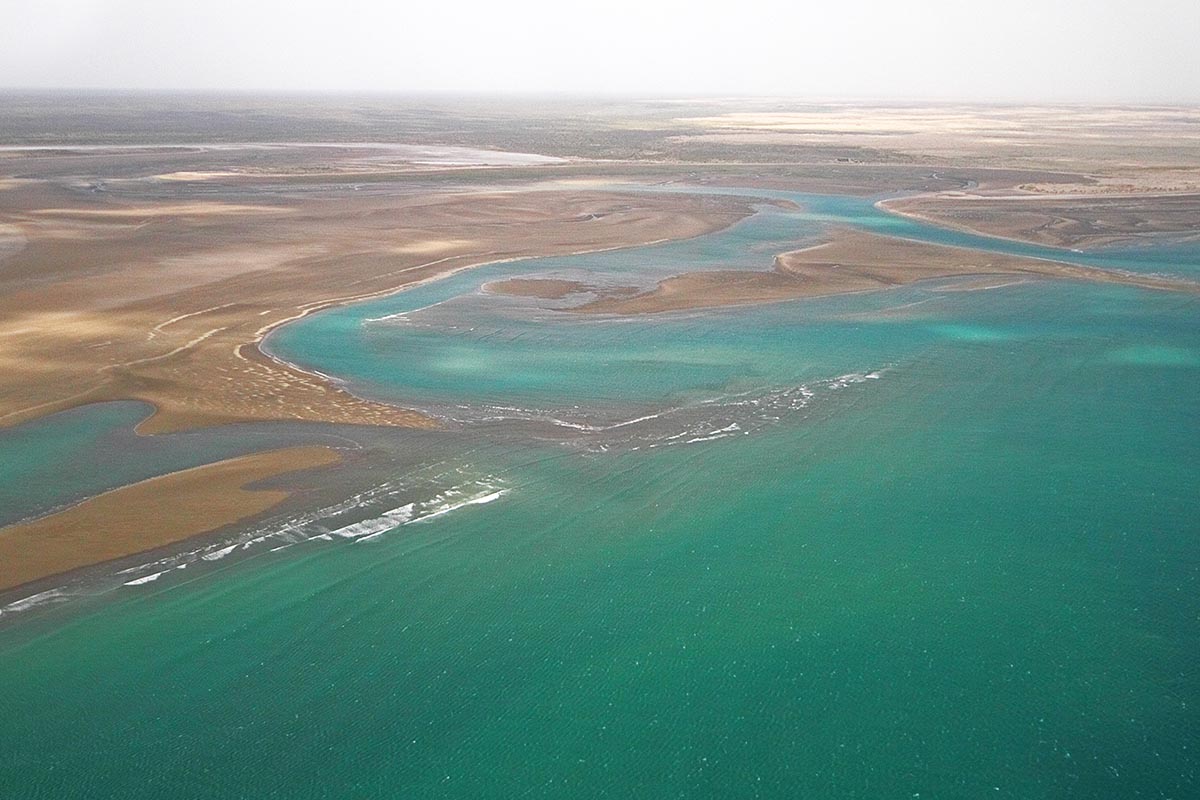
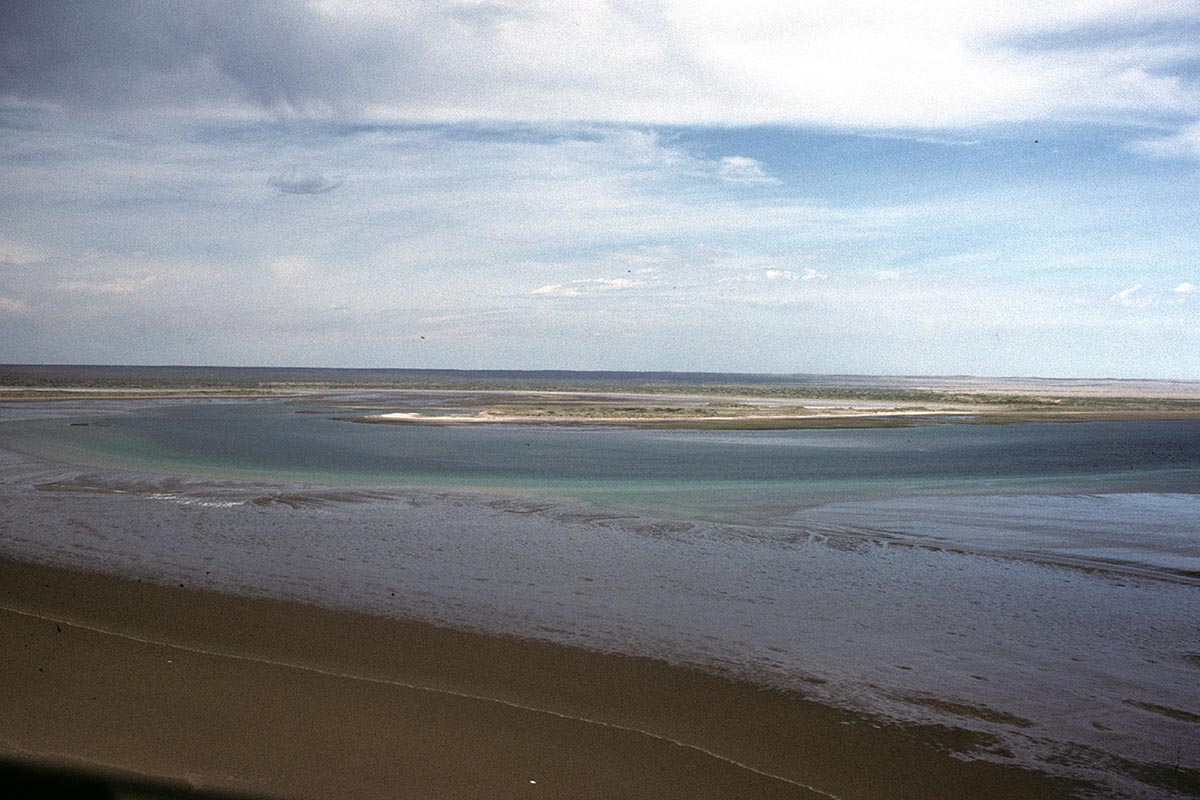
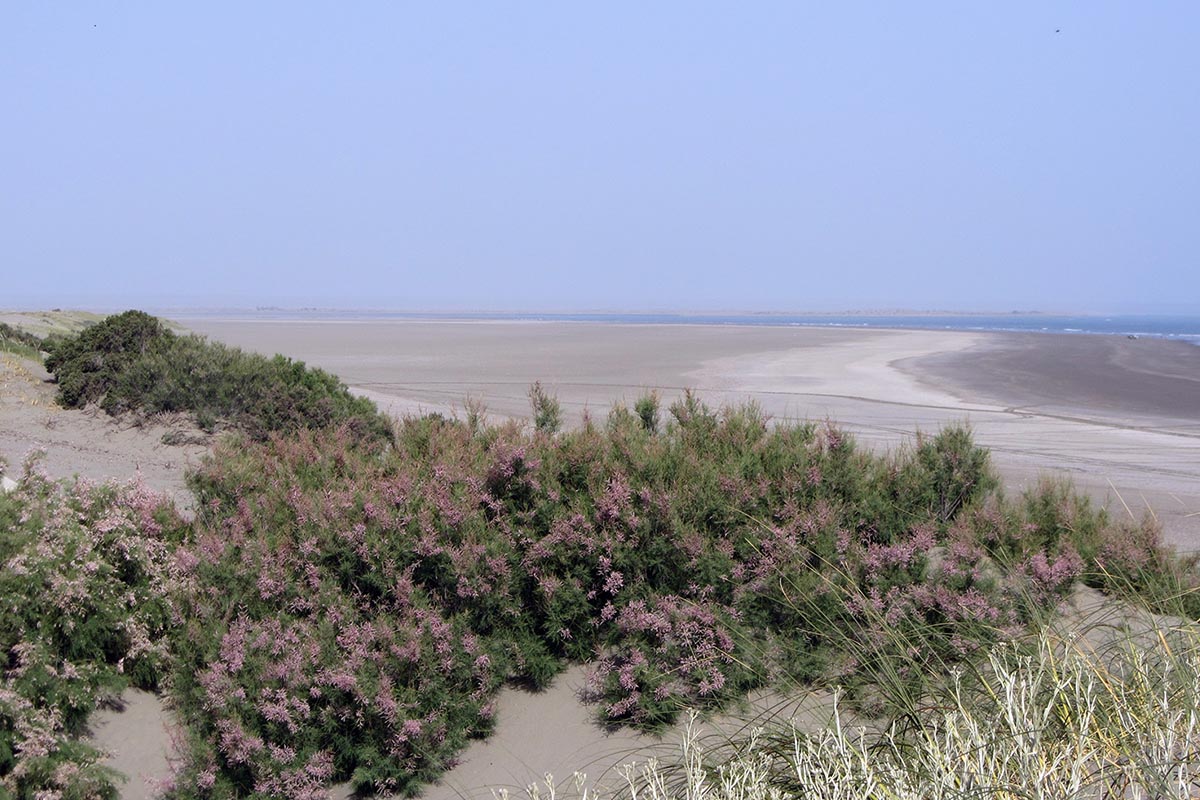
The Multiple Use Reserve “Pozo del Salado-Caleta de los Loros-Punta Mejillón” is located on the northern shore of the San Matías Gulf, east of the province of Río Negro. It extends along a front of approximately 18 km of coastline, including a marine portion, the cove and a continental portion. The reserve was created with the objective of “ensuring the conservation of the coastal sector in the face of human actions and to reconcile natural dynamics with human activity”.
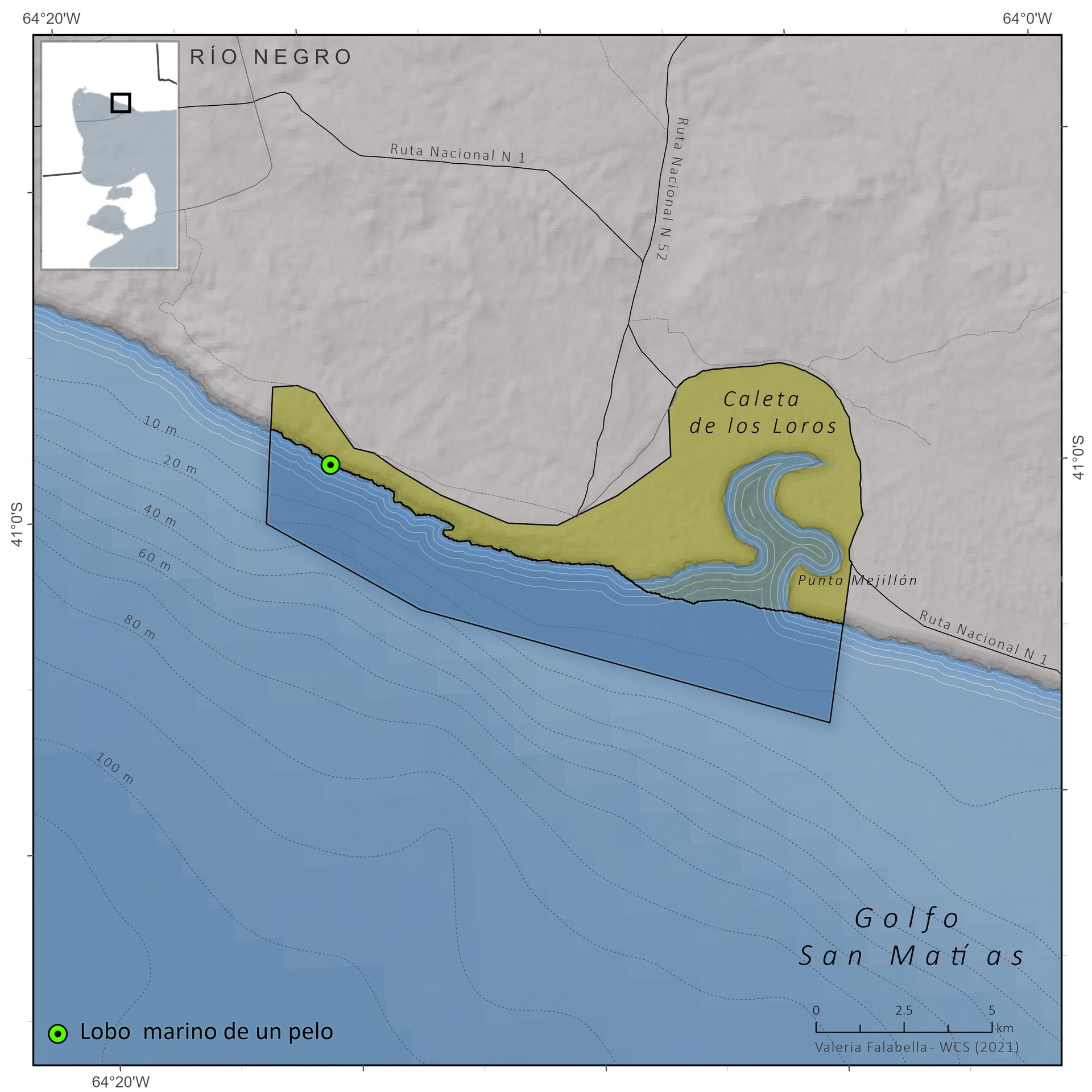
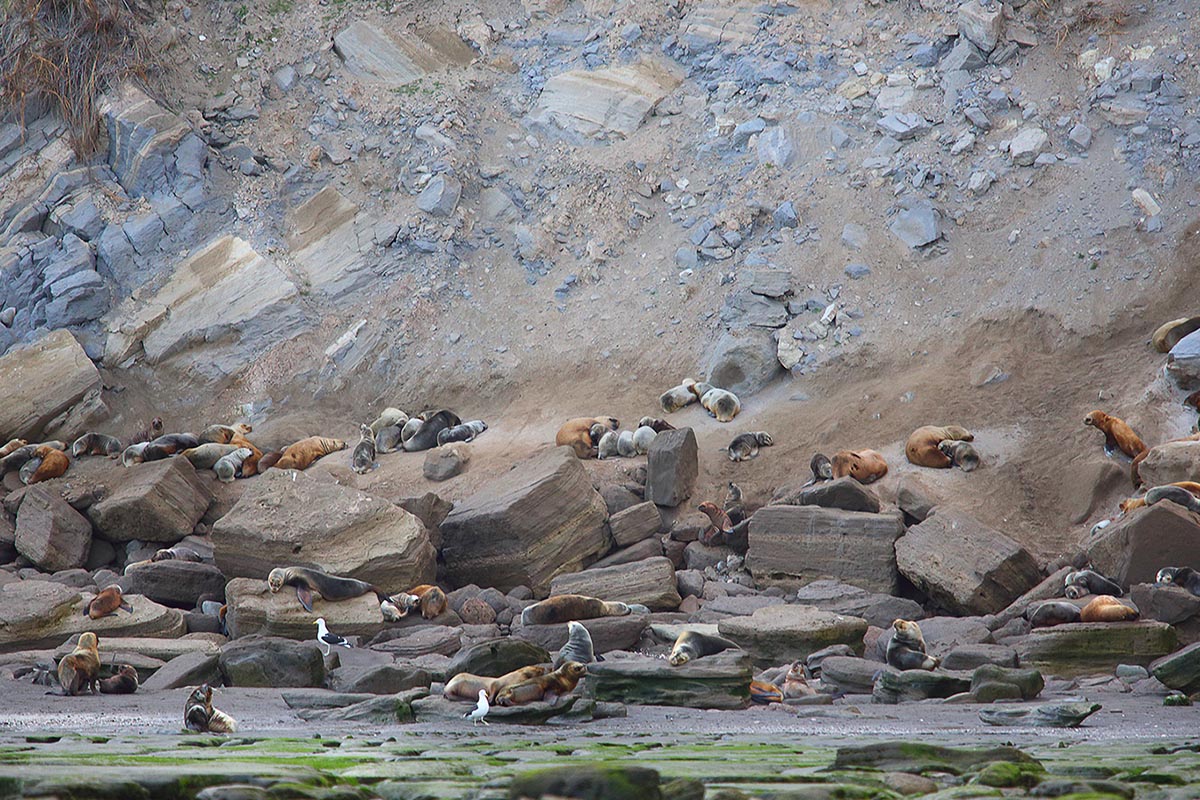
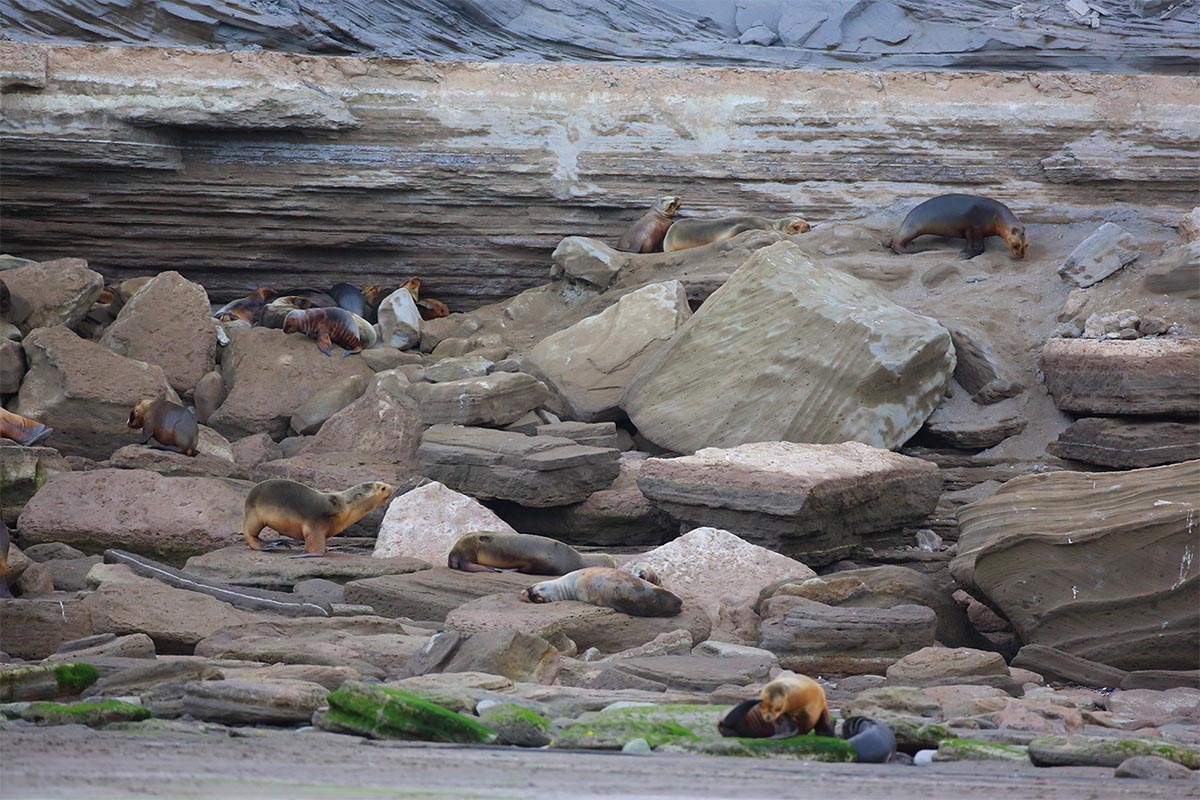
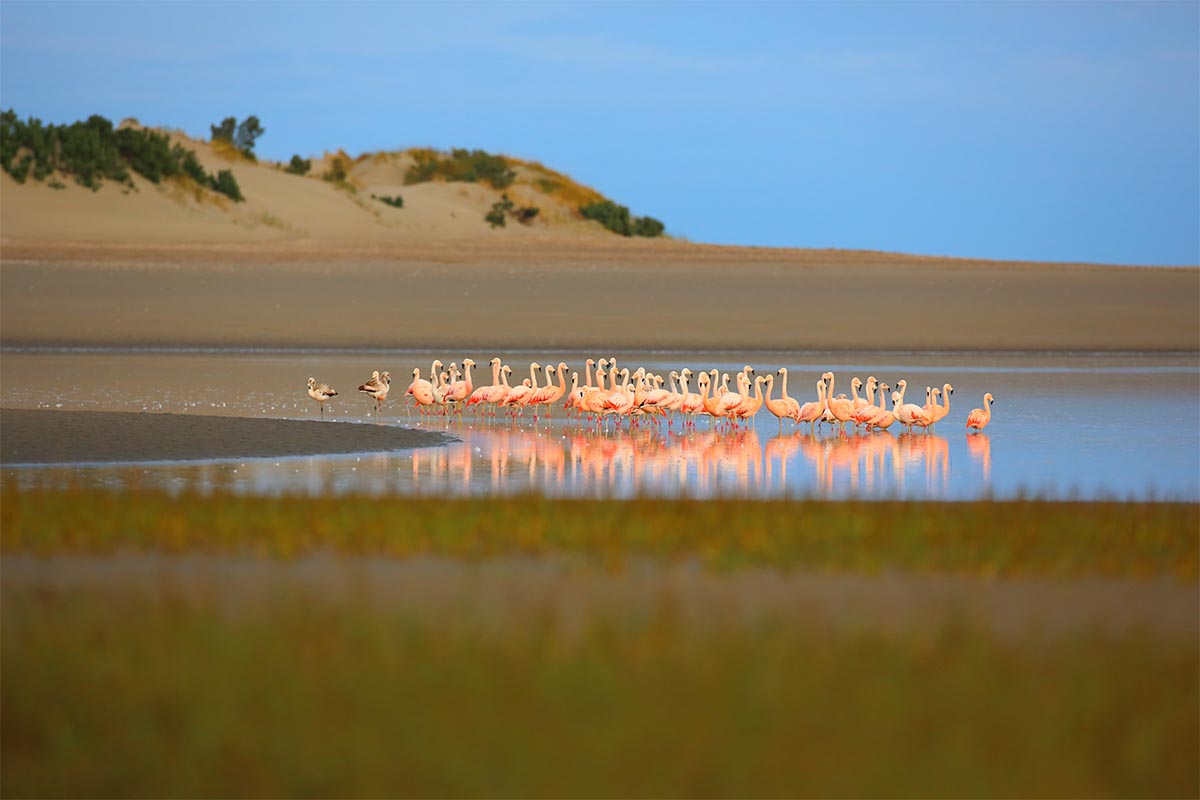
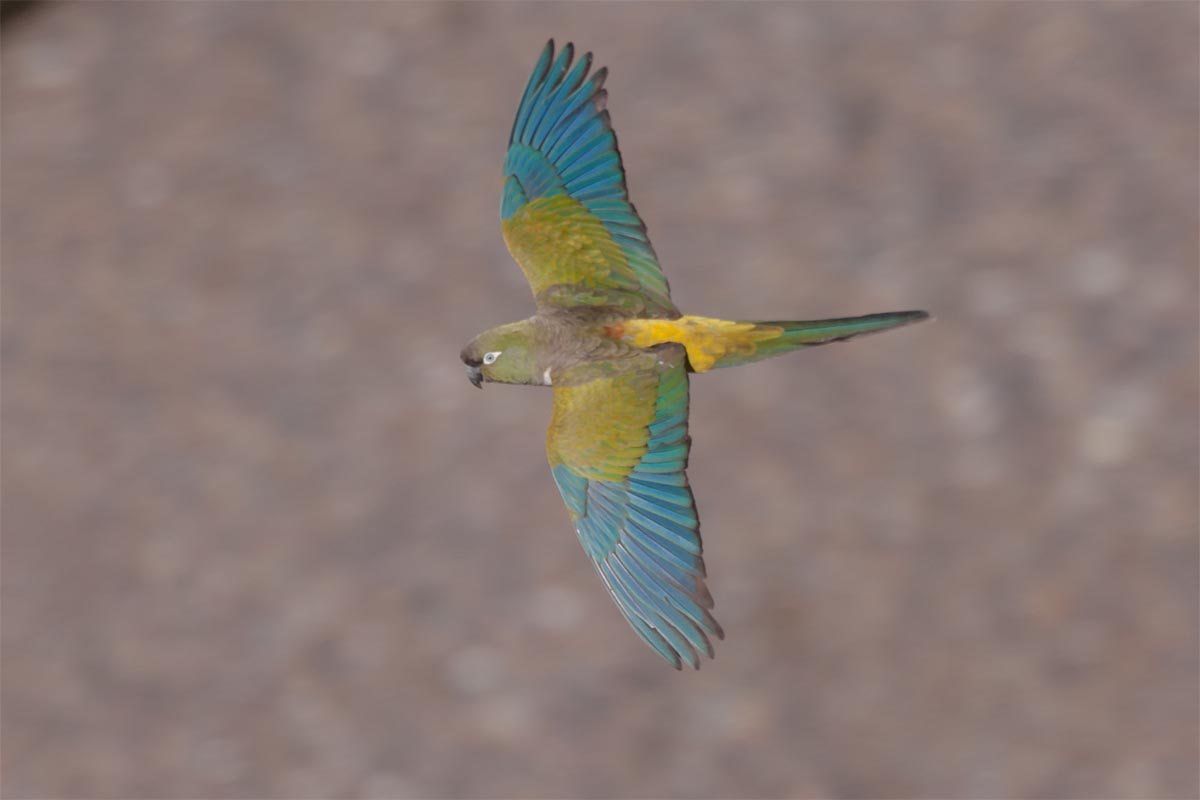
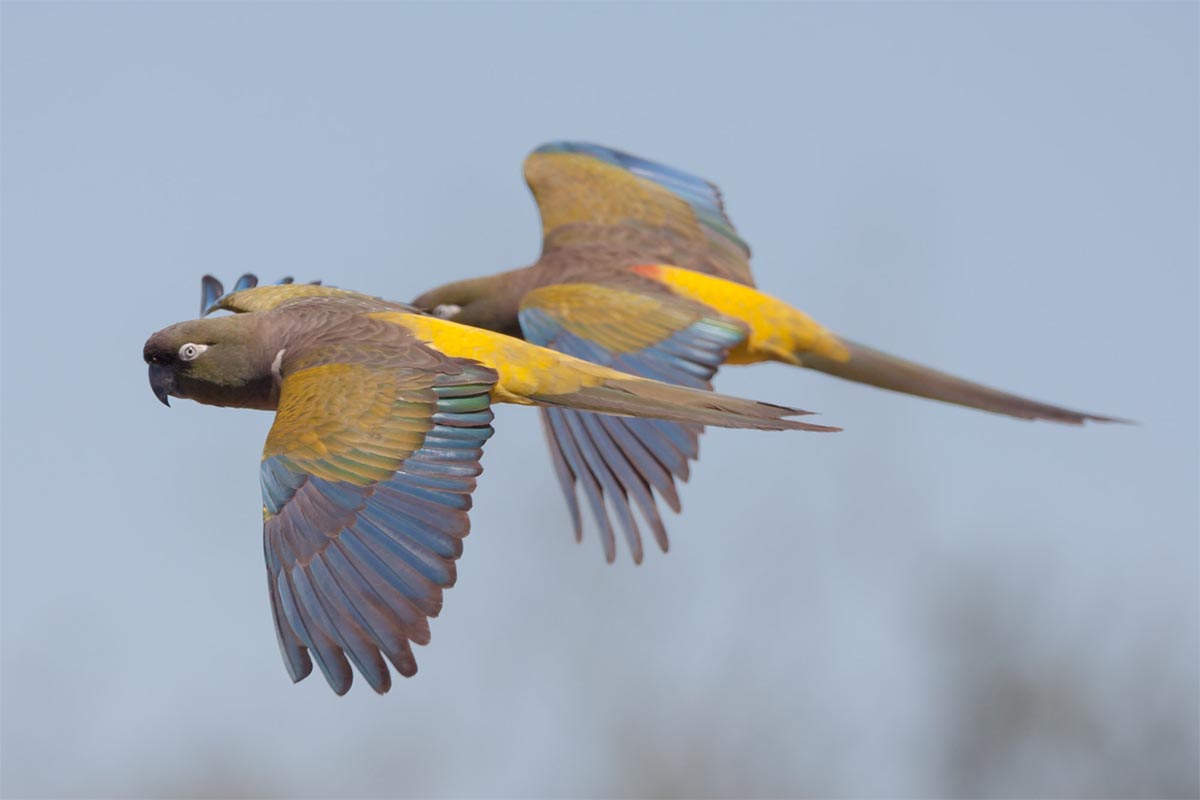
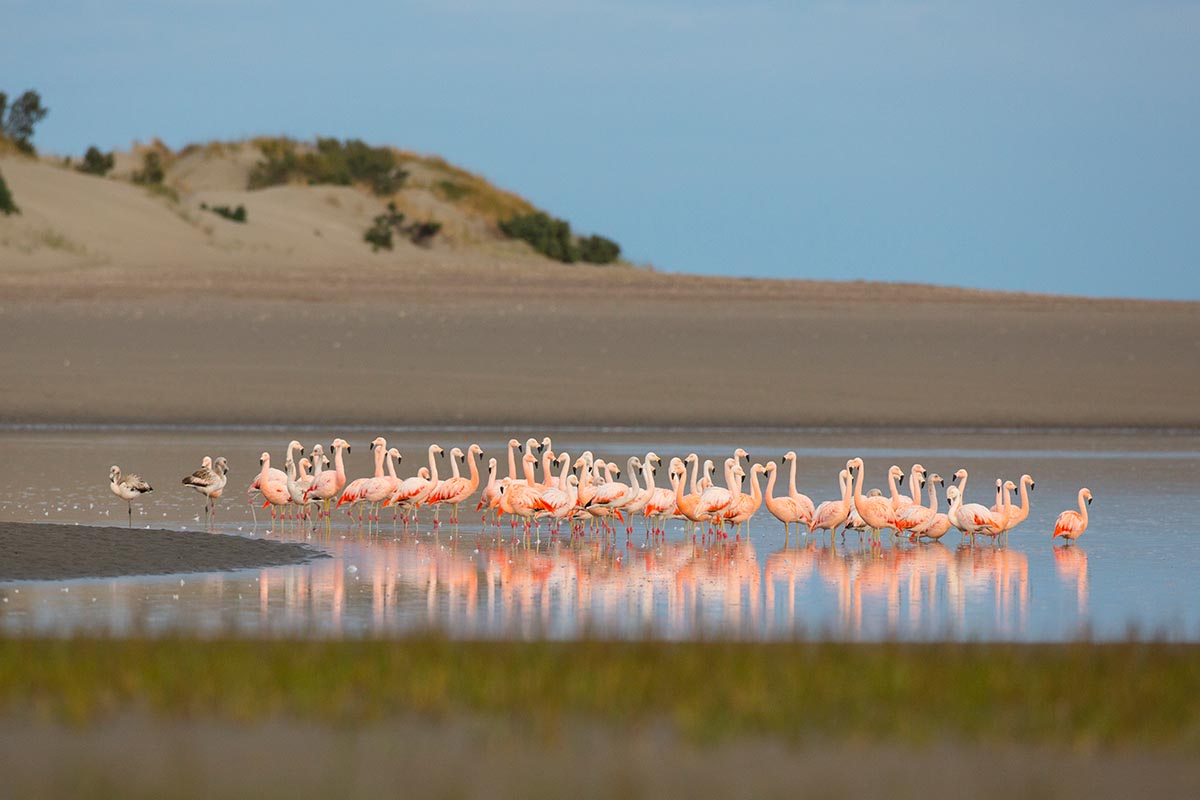
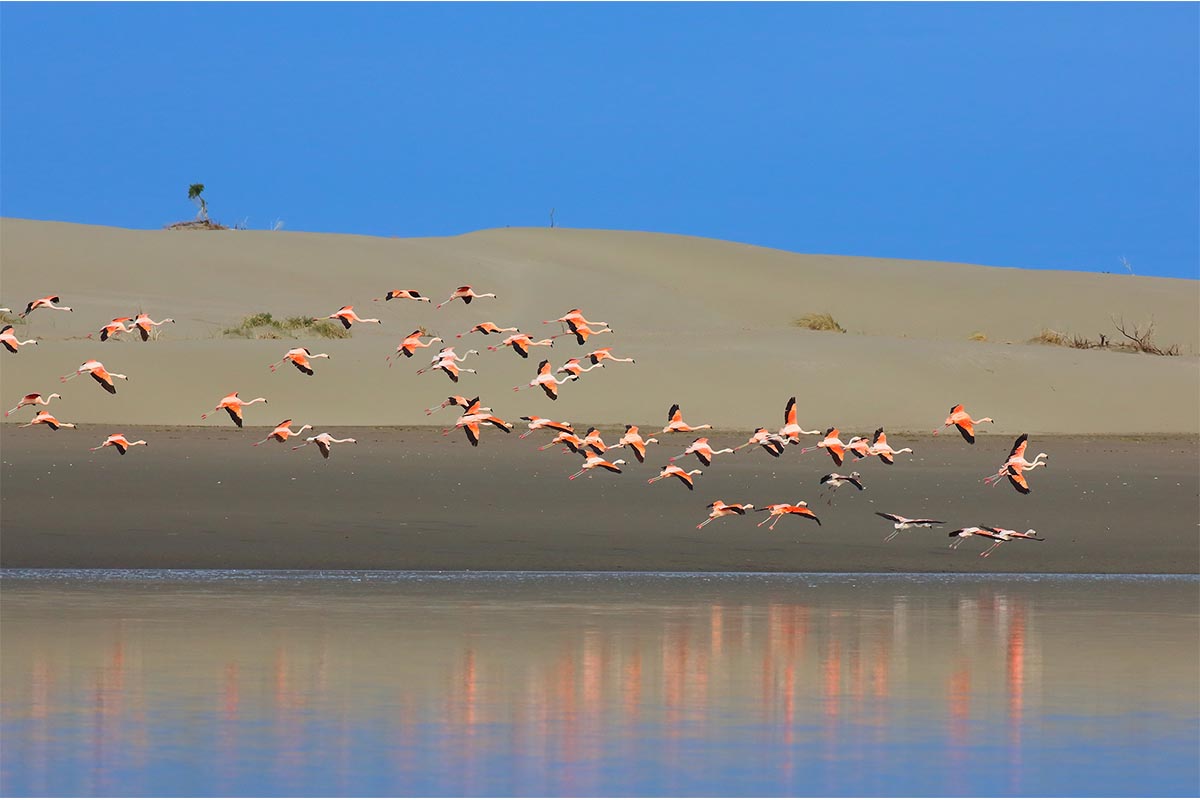
Caleta de los Loros is a site of importance for birds such as the ravine parrot, the flamingo, the gull, the gull, the gull crab, the South American tern, coscorobas, black-necked swans, among others, because it provides a sheltered environment, shallow waters and soft bottoms, which are feeding and resting areas. Another important factor is the reproductive colony of fur seals.
The continental environment is home to species of conservation interest such as the guanaco, gray fox, martinet, mara and choique, typical of Patagonian environments. The dune environments also provide special conditions for species typical of these environments.
Geographic Location
Province
Río Negro
Coordinates:
-41.03° Latitude S
-64.12° Longitude W
Size and Limits
Total Area:
Marine Area:
Continental Area:
NOTES ON SURFACE ESTIMATION
Area estimated based on the calculation of the area of the polygon represented on the map (ArcGIS PRO) with an Albers Equivalent Conic projection to preserve area calculations.
APN reports 90.84 km2 (Read More)
Rio Negro SMA specifies 90.84 total km2 and 43.20 km2 terrestrial km2
Legal Aspects
Jurisdiction
Provincial
Year of Creation
1984 / 2008
Creation Legislation
Decree Nº 1840 declares Caleta de los Loros, Pozo Salado and Punta Mejillón Multiple Use Reserve.
Provincial Law N° 3222/98 creates the Protected Area of the same name.
Provincial Law 2032/85 determines boundaries, and declares the area of Public Use subject to expropriation.


Eco-regions represented
Marine
Argentine Province
North Patagonian Gulfs Ecoregion
Land
Monte Ecoregion of plains and plateaus
Conservation Objectives
Conservation of populations of Burrowing parrots (Cyanoliseus patagonus), South American sea lions (Otaria flavescens), Southern Elephant seals (Mirounga leonina), Killer whales (Orcinus orca), and colonies of marine bivalve mollusks (Magellan mussels and scallops).(SIB)
Provide appropriate refuge for the populations of South American sea lions that inhabit Golfo San Matías.
Organize the already existing tourist activities and control their growth given limitations of infrastructure and the scarcity of water.
Regulate use of coastal resources such as marine bivalve mollusks, algae, etc.
Develop an experimental area for shellfish culture in view of the selected area’s high potential for such use, that may latter allow the experience to be extended in the region.
Provide an appropriate context for activities oriented towards environmental education to develop conservation activities. (Ambiente Rio Negro, rionegro.gov.ar)










Conservation Values
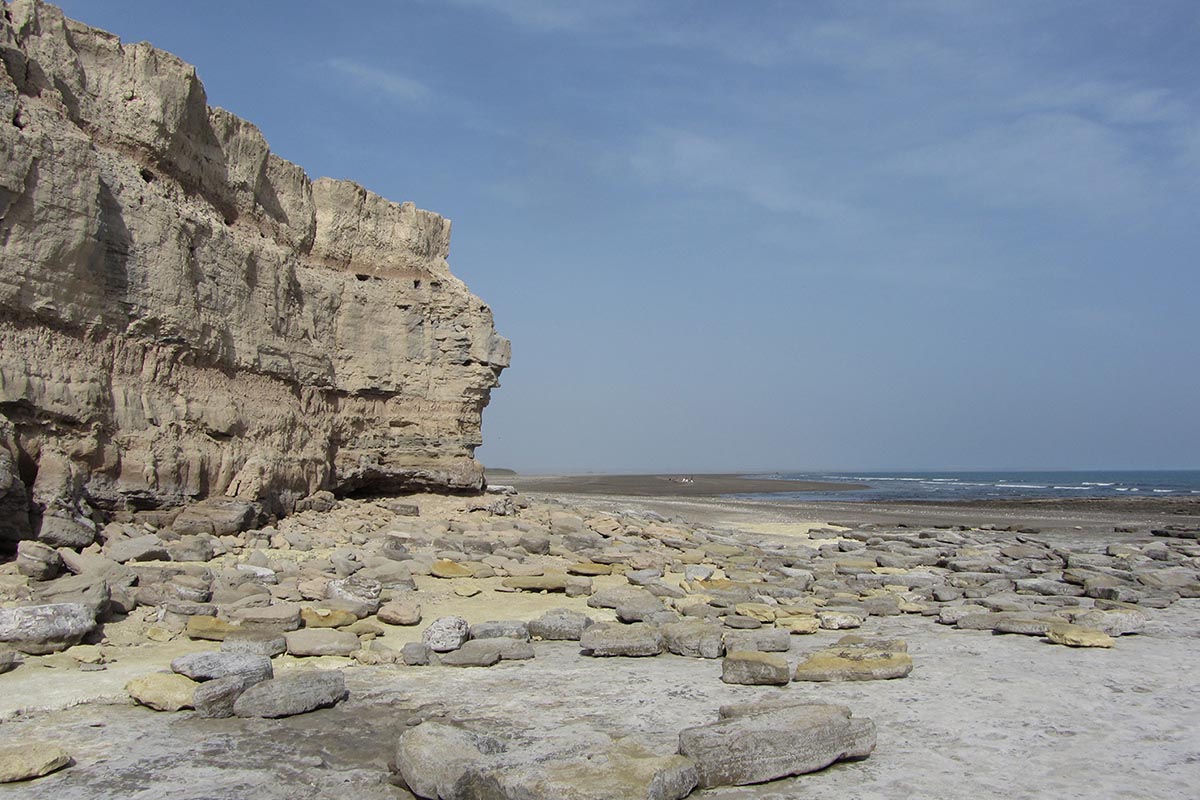
1. Cove: fossil spikes, tidal flats, bird assemblage, marshes (espartillar) and salt marshes (Sarcocornia).
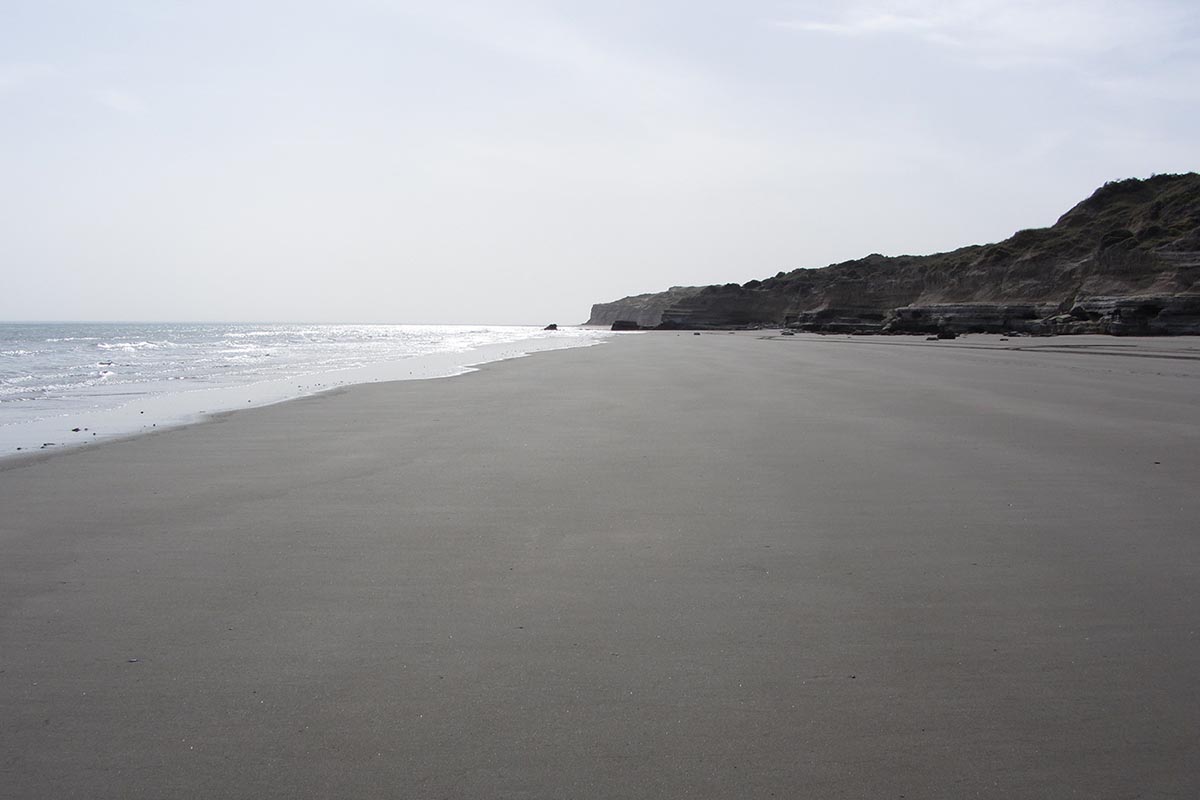
2. Coastal marine landscape: abrasion platforms, beaches, cliffs and dunes.
3. Colonies of fur seals.
4. Paleontological and archaeological heritage
Colonies and stopover sites
The following table presents the colonies or stopover sites of some emblematic species of birds and marine mammals present within the MPA boundaries.
"Too Many Requests"
Management
Year of Management Plan approval
2019
Management effectiveness and evaluation year
36 % – Evaluación METT (2014)
Sources of information consulted: Management Plan (2019).
Sea lion colonies: See Bibliography.