Cover Photo © Guillermo Harris
Description
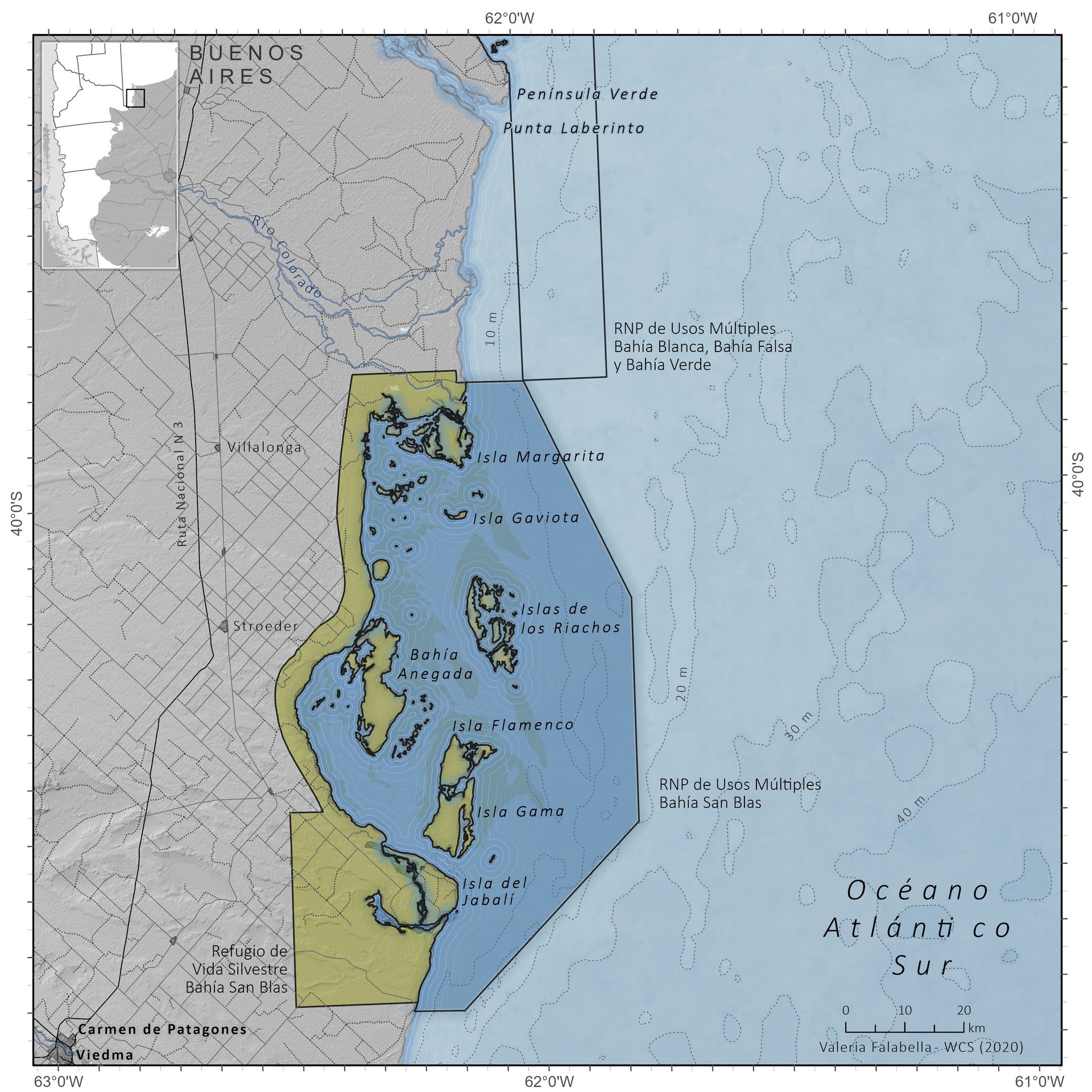
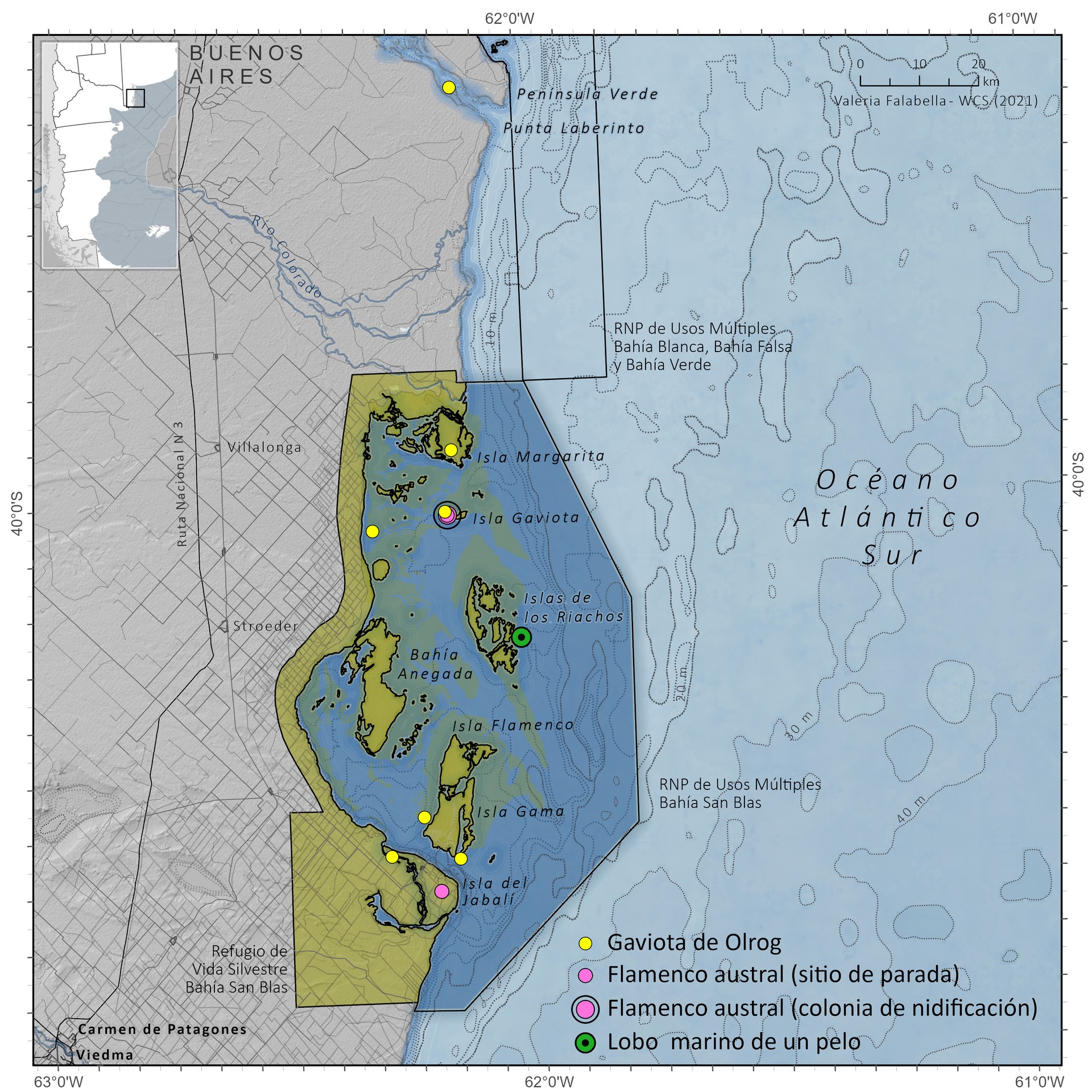
The Bahía San Blas Multiple Use Nature Reserve is located on the maritime coast of the Patagones district, in the extreme south of the province of Buenos Aires. San Blas and Anegada Bays are composed of a group of islands, banks connected by an extensive network of shallow water channels, with an extensive intertidal zone. The environment is completed with brackish water marshes, small islands and islets and other estuarine environments, with sandy beaches, other stony beaches and some coastal dunes. The vegetation corresponds to halophilic steppes (adapted to environments with little water availability). There are large crayfish beds in the area, which are feeding grounds for migratory birds. Migratory coastal birds, seabirds, marine mammals, rays, and sharks are found in the reserve. The red shorebird and Nearctic migratory species that visit the area during their migration are threatened. The area is noted for the existence of large colonies of the crabeater gull, an endemic and endangered species of the southwestern Atlantic coast. Together with the Bahía Blanca estuary ecosystem, they concentrate approximately 90% of its breeding population. The reserve’s coasts and waters are used by numerous species of marine mammals, especially the franciscana, an endemic species at great risk of extinction. The area is also home to the most important sea lion colony in the province of Buenos Aires. Its coastal waters are used by a large number of endangered species of rays and sharks.
Geographic Location
Province
Buenos Aires
Coordinates:
-40.28° Latitude S
-62.13° Longitude W
Size and Limits
Total Area:
Marine Area (Multiple Use Nature Reserve):
Superficie Continental (Wildlife Reserve):
NOTES ON SURFACE ESTIMATION
Surface area estimated based on the calculation of the area of the polygon represented on the map (ArcGIS PRO) with an Albers Conic Equivalent projection to preserve surface area calculations.
OPDS de Bs. As. reports 3910 km2 (OPDS Read More)
APN reports 1219.13 km2 for the Wildlife Refuge and 3967.48 km2 for the RNUM Read More)
Legal Aspects
Jurisdiction
Provincial
Year of Creation
1987
Creation Legislation
Provincial Law 12788 (repeals Law 10492)
Eco-regions represented
Marine
Argentine Province Ecoregion of the Buenos Aires – Uruguayan Platform
Land
Espinal Ecoregion
Conservation Objectives
Located in the Patagones district, San Blas Bay and Anegada Bay, it consists of a set of islands, banks and shallow waters, with an extensive intertidal zone. The environment is completed with brackish water marshlands, small islands and islets and other estuarial environments, with sandy and stony beaches, and some coastal dunes. The vegetation corresponds to halophilic steppes, that is, adapted to brackish environments and xerophilic scrub, and environments with little water availability. There are large mud flats, that in addition to being feeding sites for migratory birds, provide shelter for the reproduction of a great variety of marine birds.
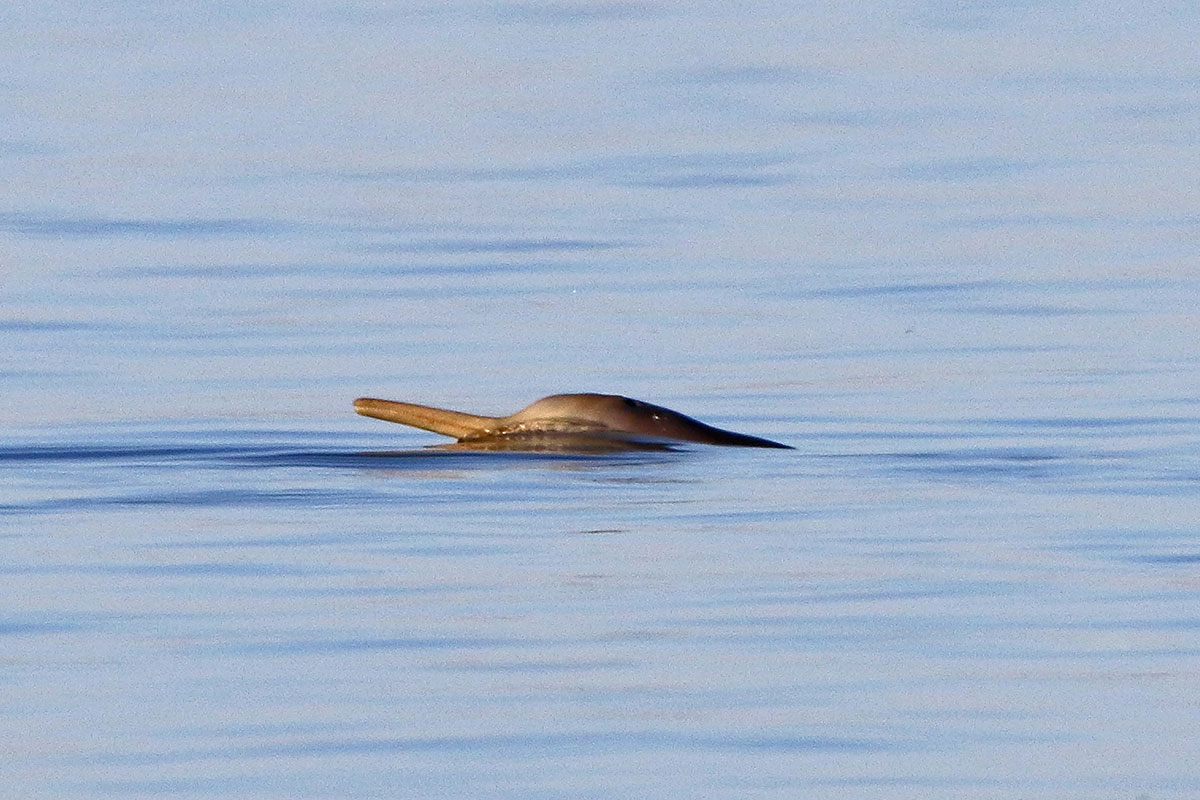
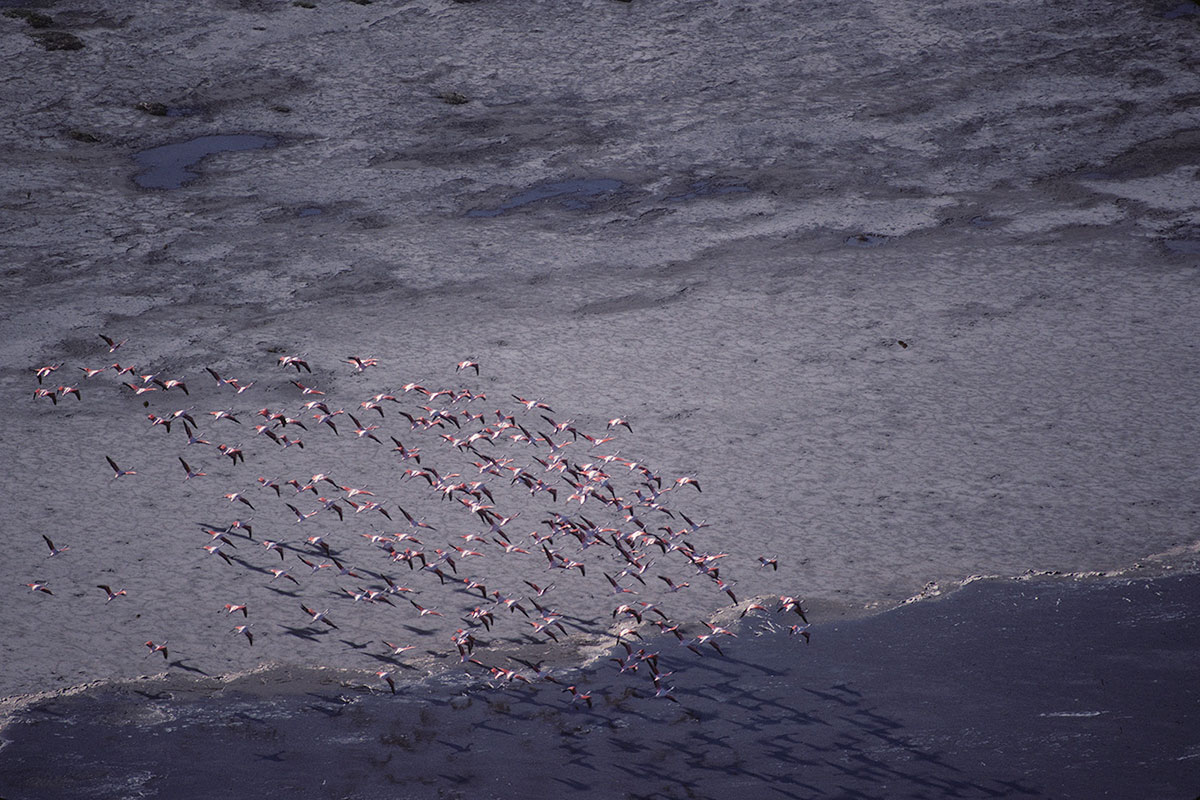







Colonies and stopover sites
The following table presents the colonies or stopover sites of some emblematic species of birds and marine mammals present within the MPA boundaries.
| ID | MPA | Specie | Scientific Name | Location | Kind of Habitat | Type of census | N | Year | Trend | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bahía Samborombón | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Punta Rasa | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |||
| 1 | Bahía Samborombón | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Punta Rasa | Sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 200 | 1997 | 1 | |
| 3 | Punta Rasa | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Punta Rasa | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |||
| 3 | Punta Rasa | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Punta Rasa | Sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 200 | 1997 | 1 | |
| 4 | Rincón de Ajo RNOD | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Bahía Samborombón (Punta Rasa) | Invernada y sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 5330 | 1994 | 1 | |
| 7 | Mar Chiquita RVS | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Albufera Mar Chiquita | Invernada y sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 600 | 1995 | 1 | |
| 7 | Mar Chiquita RVS | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Albufera Mar Chiquita | Individuos | 600 | n.a. | 1 | ||
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Embudo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 59 | 2004 | 1 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Lobos (Isla Trinidad) | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 116 | 2009 | 1,6 | |
| 12 | Islote de la Gaviota cangrejera | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla del Puerto (aka, Isla de la Punta) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 2037 | 2009 | Creciente | 1,5 |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Bastón | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Canal Ancla | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,5 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Norte | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Sur | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Luana | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 35 | 2009 | 1 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Redondo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 600 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Tres Brazas | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 829 | 2007 | 1 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Golfada Chica | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1515 | 2009 | 1 | |
| 16 | Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa y Bahía Verde | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Isla Wood | Sin nidificación | Indiciduos | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Reserva de Uso Múltiple San Blas | Sin nidificación | Individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Marina | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Gama | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,5 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Puestos | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote norte de Morro de Indio | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | 1,2,5 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Marina | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Banco Nordeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 105 | 2014 | 1,3,5 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Arroyo Jabalí Oeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 254 | 2014 | 1,2,3,4,5 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Gaviota | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 373 | 2009 | 1 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Marina | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Banco Culebra | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1244 | 2019 | 6,9 | |
| 17 | Bahía San Blas Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Isla Gaviota (Bahía Anegada) | Nidificación | Nidos | 1896 | 2020 | 2 | |
| 18 | Bahía de San Antonio Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | San Antonio Oeste | Sin nidificación | Individuos | 400 | n.a. | 1,3 | |
| 18 | Bahía de San Antonio Terrestre | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | San Antonio Oeste | Sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 800 | 1995 | 1 | |
| 18 | Bahía de San Antonio Terrestre | Red knot | Calidris canutus | San Antonio Oeste | Sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 6500 | 2005 | Decreciente | 1,2 |
| 19 | Caleta de Los Loros Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Caleta de los Loros | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 530 | 2002 | Creciente (PM del ANP 2019) | 3,9 |
| 20 | Punta Bermeja Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Bermeja | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 2836 | 2000 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 3 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Complejo Islote Lobos | Sin nidificación | Individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Marino | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Islote Lobos | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 448 | 2017 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 10,12,13 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Islote Lobos | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 448 | 2017 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 10,12,13 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Lobos | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1857 | 2002 | 3 | |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Lobos | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1857 | 2002 | 3 | |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote de los Pájaros | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Pastoza | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Redondo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote de los Pájaros | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Pastoza | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 21 | Complejo Islote Lobos - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Redondo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4748 | 2011 | Creciente | 3,19 |
| 23 | Punta Buenos Aires | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Buenos Aires | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 3049 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | P. Valdés (Playa Colombo) | Sitio de parada | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 4 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | P. Valdés (Playa Fracaso) | Sitio de parada | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 4 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | P. Valdés (Playa Fracaso) | Sin nidificación | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 5 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Península Valdés | Invernada y sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 0 | 2003 | Decreciente | 1,3 |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Hércules | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 122 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Península Valdés | Sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 130 | 1993 | 2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Larralde | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 231 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Las Charas | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 325 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Peninsula Valdés - Marino | Southern right whale | Eubalaena australis | Península Valdés | Área de reproducción y cría | Hembras reproductivas | 328 | 1990 | Creciente (decelerated rate) | 2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 |
| 24 | Peninsula Valdés - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Segunda (Caleta Valdés) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 380 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Segunda (Caleta Valdés) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 380 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Caleta Interna | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 461 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Red knot | Calidris canutus | P. Valdés (Fracasso beach) | Sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 500 | 2005 | 1,4 | |
| 24 | Peninsula Valdés - Marino | Southern right whale | Eubalaena australis | Península Valdés | Área de reproducción y cría | Individuos juveniles y mayores (ie, no crías) | 566 | 1976 | Creciente (decelerated rate) | 2,3,4,5,6,7,9,10 |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Red knot | Calidris canutus | P. Valdés (Colombo beach) | Sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 700 | 2005 | 1,4 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | La Pastosa | Total individuos | 849 | 2001 | 3 | ||
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | La Armonía | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 875 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Quiroga | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1029 | 2002 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Delgada | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 1031 | 2001 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 3 |
| 24 | Peninsula Valdés - Marino | Southern right whale | Eubalaena australis | Península Valdés | Área de reproducción y cría | Individuos dentro de la franja costera | 1200 | 2011 | Creciente (decelerated rate) | 4,6,7,8,9,10 |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Pirámide | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1349 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Morro Nuevo | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1546 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Asentamiento Oeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1621 | 2003 | creciente | 2,3 |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Buenos Aires | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 3049 | 2001 | 3 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Norte | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 4218 | 2001 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 6 |
| 24 | Peninsula Valdés - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Primera (Caleta Valdés) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 12539 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Primera (Caleta Valdés) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 12539 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Caleta Externa | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 40225 | 2009 | creciente | 2,3,19 |
| 24 | Península Valdés - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Estancia San Lorenzo (aka, Punta Norte) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 134416 | 2008 | creciente | 2,3,9,17,19 |
| 26 | Punta Loma | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Loma | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 488 | 2002 | 3 | |
| 27 | Punta León - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta León | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 3212 | 2001 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 3 |
| 27 | Punta León - Terrestre | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Punta León | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 5617 | 2016 | Creciente | 1,2,6 |
| 28 | Punta Tombo - Terrestre | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Punta Tombo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 372 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 28 | Punta Tombo - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Punta Tombo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 201000 | 2014 | Decreciente | 2,3,811,16,18,19 |
| 29 | Punta Tombo - Marina | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Chato | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 461 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 30 | Cabo Dos Bahías | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Cabo Dos Bahías | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 12295 | 2010 | 1,2,19,21 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Felipe | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | n.a. | 2009 | Estable | 1,2,5 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Sin Nombre | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | n.a. | 2009 | Estable | 1 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Vernaci Oeste Noroeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | n.a. | 2009 | Estable | 1,5,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Norte del Golfo San Jorge | Sin nidificación | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo Dos Bahías | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 10 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Vernaci Noroeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | Estable | 1,5 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Isla Vernaci Sudoeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | Estable | 1,2,5 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Laguna | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | Estable | 1,2,5 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Olrog's gull | Larus atlanticus | Islote Luisoni | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2009 | Estable | 1,5 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Isabel Sur | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2016 | Decreciente | 1,2,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Aristizábal | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 11 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Castillo | Total individuos | 15 | 1990 | 4 | ||
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Vernacci Este | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 18 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Goëland | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 18 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Este | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 28 | 2001 | 1,2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Sudoeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 52 | 2003 | Creciente | 2,3,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Península Lanaud | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 72 | 2016 | Decreciente | 1,2,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Pan de Azúcar | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 76 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Galiano Norte | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 120 | 1990 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Moreno | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 131 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Moreno | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 131 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Vernaci Este | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 144 | 2016 | Decreciente | 1,2,3,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Fondo 1 | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 162 | 1998 | Creciente | 2,3,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Buque | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 174 | 1994 | Decreciente | 2 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Vernaci Oeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 178 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Fondo 2 | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 219 | 2003 | Creciente | 2,3,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Arellano | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 235 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Moreno | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 242 | 1994 | 2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Moreno | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 242 | 1994 | 2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Leones | Total individuos | 270 | 1990 | 4 | ||
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Gran Robredo | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 271 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Ezquerra | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 271 | 2016 | Decreciente | 1,2,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Noroeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 275 | 2003 | Decreciente | 2,3,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Vernacci Oeste | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 279 | 1989 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Tovita | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 282 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Puente | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 319 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Moreno | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 380 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Moreno | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 380 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Islotes Arellano | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 385 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote Guerrico | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 480 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Bahía Bustamante | Invernada y sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 490 | 1999 | 1,3 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Este | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 528 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Sur | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 542 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Islote Puente | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 574 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Islas Lobos | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 669 | 2016 | Decreciente | 1,2,6 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Tovita | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 693 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Sudoeste | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 775 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Sudoeste | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 867 | 1995 | Decreciente | 2 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Lobos | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 876 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Pequeño Robredo | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 917 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Gaviota | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 939 | 2001 | 1,2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Galiano Sur | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 991 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Vernacci Sudoeste | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1163 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Gran Robredo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1342 | 2016 | 1,2,6 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Quintano | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1558 | 2016 | 1,2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Quintano | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 2303 | 1995 | 4 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Este | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 2503 | 2003 | Decreciente | 2,3,17,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Norte 2 | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 5183 | 2003 | Creciente | 2,3,17,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Península Lanaud | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 5460 | 1995 | Decreciente | 2 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Bahía Bustamante | Sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 6900 | 1988 | 1 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Cabo Dos Bahías | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 12295 | 2010 | 1,2,19,21 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Vernaci Norte 1 | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 24105 | 2003 | Decreciente | 2,3,17,20 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Tovita | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 31906 | 2001 | 1,2 | |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Leones | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 45842 | 2009 | Decreciente | 2,3,19 |
| 31 | Patagonia Austral - Marino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Tova | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 57174 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 32 | Punta del Marquéz - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta del Marqués | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 2120 | 2014 | 10,11 | |
| 36 | Monte Loayza - Terrestre | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Monte Loayza (aka, Bahía Sanguineto) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 37 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,7 |
| 36 | Monte Loayza - Marino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Monte Loayza | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1400 | 1999 | 1,2,7 | |
| 36 | Monte Loayza - Terrestre | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Monte Loayza | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1972 | 2012 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 5,6 |
| 37 | Cabo Blanco | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Cabo Blanco | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 0 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 37 | Cabo Blanco | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo Blanco | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 22 | 2011 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 37 | Cabo Blanco | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Cabo Blanco | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 23 | 2003 | stable | 1,2,7 |
| 37 | Cabo Blanco | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo Blanco | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 36 | 2012 | 5,6 | |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Islote de C. del Puerto | Colonia | n.a. | 2003 | Estable | 1,7 | |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Punta Piedrabuena | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 11 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,5,7 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Cañadón del Indio (aka, C. del Indio II) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 22 | 1993 | 2,5,7 | |
| 38 | Ría Deseado | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Cañadón del Puerto | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 44 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,5,7 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Isla del Rey | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 45 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,5,7 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Cañadón Torcido (aka, C. del Indio I) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 46 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,5,7 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Larga | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 50 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Isla Elena | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 105 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,4,5,7 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Burlotti | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 225 | 1993 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Estuario Río Deseado | Sitio de parada | Individuos (high count) | 520 | 1988 | 1 | |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Cañadón del Puerto | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 580 | 1992 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla del Rey | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1100 | 1993 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Quiroga | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1400 | 2018 | Creciente | 2,3,6 |
| 38 | Ría Deseado - Ría | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla de los Pájaros (Ría Deseado) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 8650 | 1993 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Islote del Cabo | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | n.a. | n.a. | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 10 |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Islote Castillo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 22 | 1998 | Estable | 1,2,7 |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote del Cabo | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 40 | 2012 | 5,6 | |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Islote Sur de Islote del Cabo | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 102 | 1999 | 1,2 | |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote Sin Nombre | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 400 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 39 | PIM Isla Pingüino | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote frente a Punta Medano Negro | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1322 | 2012 | 5,6 | |
| 40 | Bahía Laura | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Islote del Bajío | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 175 | 1994 | creciente | 2,3 |
| 40 | Bahía Laura | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Cabo Guardián | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 7000 | 1994 | creciente | 2,3 |
| 41 | Isla Cormorán y Justicia | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Banco Justicia I | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 30 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3,17 |
| 41 | Isla Cormorán y Justicia | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Banco Justicia I | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1377 | 1999 | 1,2 | |
| 41 | Isla Cormorán y Justicia | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Banco Cormorán | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 37150 | 1993 | Creciente | 2,3,17 |
| 42 | Península San Julián | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Bahía San Julián | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |||
| 43 | Bahía San Julián - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Banco Justicia I | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 30 | 1994 | creciente | 2,3,17 |
| 43 | Bahía San Julián - Terrestre | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Banco Justicia I | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1377 | 1999 | 1,2 | |
| 43 | Bahía San Julián - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Banco Cormorán | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 37150 | 1993 | creciente | 2,3,17 |
| 44 | PIM Makenke | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Makenke | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 626 | 2012 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 5 |
| 45 | Isla Leones | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Leones | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1788 | 1999 | 1,2 | |
| 45 | Isla Leones | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Leones | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 19200 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 46 | Isla de Monte León | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla de Monte León | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1375 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 47 | Monte León | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Cuevas de Monte León | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 3 | 2003 | Estable | 1,2,7 |
| 47 | Monte León | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cerro Monte León | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 100 | 2012 | 2,5 | |
| 47 | Monte León | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Sur de Rincón del Buque II | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 110 | 2003 | 1,2 | |
| 47 | Monte León | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Observación | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 270 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 47 | Monte León | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Cuevas o N de Cerro Observatorio | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1194 | 2012 | 2,5 | |
| 47 | Monte León | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Sur de Rincón del Buque | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 3437 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 47 | Monte León | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Monte León | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 32000 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 48 | Isla Deseada | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Deseada | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 3560 | 1995 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| 48 | Isla Deseada | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Deseada | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4503 | 1997 | 1,2 | |
| 49 | Aves Migratorias | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Río Gallegos | Invernada y sitio de parada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 1000 | 2005 | 1 | |
| 49 | Aves Migratorias | Chilean flamingo | Phoenicopterus chilensis | Estuario de Río Gallegos | n.a. | n.a. | 1 | |||
| 50 | Río Gallegos | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Río Gallegos | Invernada | Individuos (high count) | 1000 | 2002 | 1 | |
| 51 | Cabo Vírgenes | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Cabo Vírgenes | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 146000 | 2019 | creciente | 2,3,7,11 |
| 52 | Costa Atlántica Tierra del Fuego | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Bahía San Sebastian | Invernada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 100 | 2005 | Decreciente | 1 |
| 52 | Costa Atlántica Tierra del Fuego | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo Santa Inés | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 221 | 1994 | 5 | |
| 52 | Costa Atlántica Tierra del Fuego | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Río Grande | Invernada | Individuos (high count) | 287 | n.a. | 1 | |
| 52 | Costa Atlántica Tierra del Fuego | Red knot | Calidris canutus | Río Grande | Invernada | Individuos (conteo máximo) | 5000 | 2005 | Estable | 1,2 |
| 52 | Costa Atlántica Tierra del Fuego | Hudsonian godwit | Limosa haemastica | Bahía San Sebastian | Invernada | Individuos (high count) | 19340 | 1989 | 1 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Bahía Flinders | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 0 | 2012 | 2,6,8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Bahía Flinders | Total individuos | 0 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,3,10 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo San Antonio | Total individuos | 0 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,3,10 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Rocas Miretti | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1 | 1995 | 1,2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Islote menor de Islote Fabián | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 3 | 1995 | 1,2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Zapata | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 3 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Leguizamo N and S | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 4 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Roca Tevez | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 7 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Fallows | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 10 | 1997 | 2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Islote San Juan | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 11 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Punta Jira | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 11 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo Brizuela | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 16 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Caleta Ojeda | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 17 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo Brizuela | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 17 | 2012 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 3,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo San Juan | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 20 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo Forneaux | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 23 | 2012 | 8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Este de Punta Shank | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 31 | 1997 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Sur de Punta Pañuelo | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 42 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Goffré | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 50 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Dorgambide y Punta Shank | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 86 | 1995 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Isla Observatorio | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 100 | 1995 | 2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Fallows | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 114 | 2012 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Cabo San Antonio | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 129 | 2012 | 2,6,8 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Cabo San Juan (Isla de los Estados) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 150 | 2020 | 5 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo San Juan | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 177 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Zapata | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 185 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Achaval | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 223 | 2012 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Islote San Juan | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 251 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Isla Barrionuevo | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 253 | 2012 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Rocas Tevez | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 274 | 2012 | Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Caleta Ojeda | Sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 333 | 1997 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Leguizamo | Colonia reproductiva y sitio de descanso | Total individuos | 827 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Bahía Paz | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 898 | 2001 | 1 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Cabo Furneaux | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1518 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 1,2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Bahía Franklin (Isla de los Estados) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 1633 | 2010 | creciente | 4 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Isla Observatorio | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 2587 | 1994 | 1,2 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Imperial shag | Leucocarbo atriceps | Bahía Franklin | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 4592 | 2013 | 9 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | South American fur seal | Arctocephalus australis | Punta Jira | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 5339 | 2012 | Tendencia creciente para el archipiélago fueguino como un todo (hay desplazamiento de individuos entre distintas colonias, Milano et al 2020). Ligeramente creciente a nivel regional (Cardenas et al 2016) | 2,3,4,10 |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Southern rockhopper penguin | Eudyptes chrysocome | Cabo San Juan (Isla de los Estados) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 7031 | 1999 | 3,5,6 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Goffré (Islas de Año Nuevo) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 14849 | 1995 | 1 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Isla Observatorio (Islas de Año Nuevo) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 105534 | 1995 | 1 | |
| 54 | Isla de los Estados | Southern rockhopper penguin | Eudyptes chrysocome | Bahía Franklin (Isla de los Estados) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 127325 | 2010 | Decreciente | 4,5,6 |
| 59 | Cañadón del Duraznillo | Red-legged cormorant | Phalacrocorax gaimardi | Monte Loayza (aka, Bahía Sanguineto) | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 37 | 2003 | stable | 1,2,7 |
| 59 | Cañadón del Duraznillo | South American sea lion | Otaria flavescens | Monte Loayza | Colonia reproductiva | Total individuos | 1972 | 2012 | Creciente (G. Harris pers comm) | 5,6 |
| 62 | Pingüinos - Terrestre | Magellanic penguin | Spheniscus magellanicus | Punta Pájaros | Colonia | Parejas reproductivas | 300 | 1994 | Creciente | 2,3 |
| ID | MPA | Specie | N | Year |
Management
Management effectiveness and evaluation year
34 % – METT Evaluation (2014)
Year of Management Plan approval
2008
Sources of information consulted: Management Plan (2008).
Bird and marine mammal colonies: See bibliography

